- 25 July 2023
Gatekeeper & Runtime Protection in macOS: A Secure Software

Introducing Gatekeeper: Ensuring Trusted Software
Gatekeeper is a security technology integrated into macOS, Before running any software, Gatekeeper verifies its authenticity and allows execution only if it meets the criteria. When a user downloads and opens an app, plug-in, or installer package from sources outside the App Store, Gatekeeper performs several essential checks like:
Developer Verification:
Gatekeeper confirms whether the software comes from an identified developer. This helps prevent the execution of unauthorized or potentially harmful software.
Notarization by Apple:
App notarization is performed by Apple as a means to confirm their lack of known malicious content This notarization process is examined by Gatekeeper to determine if the downloaded software has completed it.
Unaltered Software:
Gatekeeper ensures that the software has not been altered or tampered with after being downloaded. This gives an added safeguard against potential risks.
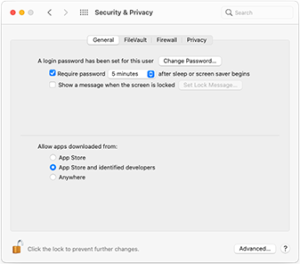
Configuring Gatekeeper Preferences for Users and Organizations for Users and Organizations
macOS grants users and organizations the flexibility to customize Gatekeeper settings based on their security preferences and requirements:
App Store Restrictions:
Users can decide to exclusively permit software installations sourced specifically from the App Store.. This provides an extra layer of security Security is enhanced by restricting app sources solely to Apple’s carefully selected and monitored platform.
Mobile Device Management (MDM) Overrides:
Organizations can utilize MDM solutions to surpass Gatekeeper policies and facilitate the running of software as long as there are no explicit limitations. Efficiently managing software distribution is made possible through this feature.
Alternate Identity Signatures:
MDM configurations can also permit software signed with alternate identities, facilitating specific use cases while maintaining security protocols.
Disabling Gatekeeper:
Under exceptional circumstances, where certain applications require unrestricted access, disabling Gatekeeper is an option. Nevertheless, one must proceed with care, since it eliminates the safeguard against unverified software .
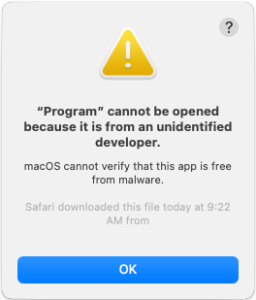
How Gatekeeper Works: Verification and User Approval
Once a user starts to open recently downloaded software, Before executing, Gatekeeper asks the user for approval. This preventive measure ensures so that users have knowledge of the software’s origin. The user hasn’t been deceived into running potentially harmful code disguised as harmless data.
By default, macOS configures Gatekeeper to allow only software from the App Store or signed by registered developers with notarization by Apple. By thoroughly inspecting apps, both the App Store review process and notarization pipeline actively work to detect and eradicate known malware, Thus, users are assured of a protected app environment.
Runtime Protection: Safeguarding System Files and App Sandbox
Moreover, macOS implements runtime security measures that defend crucial system files, resources, and the kernel against unauthorized access by user applications. Data privacy is ensured and security is enhanced as this isolation prevents apps from accessing data stored by other apps.
Apps downloaded from the App Store operate within a sandboxed environment, Their ability to reach out and use resources beyond the specified container is restricted. Should an application necessitate data retrieval from another application, it can only do so through macOS-provided APIs and services, preventing unauthorized data access.
Conclusion
Gatekeeper and runtime protection in macOS work collaboratively to deliver a secure computing experience to Mac users. Gatekeeper ensures that only verified and trusted software runs on the system, Minimizing potential risks associated with malware and unauthorized code execution forms part of Gatekeeper’s purpose. Moreover, runtime defense defends vital system elements and implements application sandboxing to enhance the privacy and security of data. By incorporating these robust security measures, Users and organizations are empowered by macOS to through offering a trustworthy and stable platform for computing.

