- 26 July 2023
- 142
Managing Windows Update for Business with Group Policy

Introduction to Windows Update for Business
IT administrators have access to a robust tool called Windows Update for Business enabling IT administrators to effectively manage and control updates on devices running both Windows 10 and Windows 11 within an organization. Utilizing the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), administrators have a powerful tool to handle update deployment and reception on devices in an efficient manner.
Establishing Windows Update for Business utilizing Group Policy with Group Policy
To ensure the effective establishment of Windows Update for Business, creating deployment rings that are in line with the organization’s update deployment strategy is crucial. Different groups of devices can receive updates at specific stages of deployment using deployment rings. To give an instance, rings may be created for initial testers, extensive rollout and crucial devices.
To begin, launch the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc) on a device running Remote Server Administration Tools or on a domain controller. Administrative Templates in Computer Configuration provide options to customize Windows Update settings, relevant policies for Windows Update for Business can be configured.
Controlling Feature and Quality Updates
To effectively handle the updates available for devices, administrators can decide to enable Microsoft Updates and drivers specifically for Windows Update for Business. Updates for other Microsoft products are included in Microsoft Updates, Automatic driver enablement occurs on device systems.
Administrators can also control when devices receive feature and quality updates. To get a sneak peek at the upcoming feature updates, especially for those who are interested, enrolling in the Windows Insider Program for Business is recommended. Group Policy Management Console Preview builds and feature updates can be managed using this tool..
For deferring or pausing updates, Feature updates can be delayed for a maximum of 365 days by setting policies as per administrator’s discretion. They can also delay quality updates for up to 30 days. To guarantee that devices receive updates solely once they have undergone extensive validation.
Managing User Experience with Updates
For optimal user satisfaction, it is commonly suggested to let updates be installed automatically. The default settings allow for setting this behavior. For increased control, active hours can be specified by administrators to prevent updates from being installed. To achieve precise control, automatic updates can be scheduled to install at specific times.
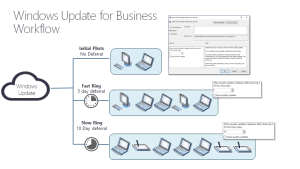
In order to fulfill security and compliance obligations, those in charge can establish deadlines for automated updates as well as restarts pertaining to both feature upgrades and quality enhancements. This policy ensures devices stay up-to-date and secure.
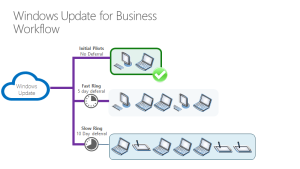
Another option is to customize update notifications. is also possible. Administrators can choose from different notification settings, like the option to deactivate all notifications or exclusively show restart warnings. Finding the right equilibrium between user experience and compliance is crucial while adjusting the notification configuration.
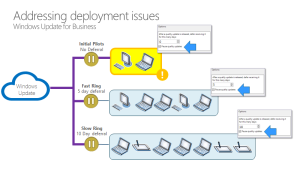
Admins can also control the update settings accessible to users. Restricting the ability to pause updates can be achieved through Group Policy, The delay of updates for extended periods can be prevented for users.
Enabling Features Introduced via Servicing
Commencing at Windows 11, version 22H2, new features and enhancements are introduced through monthly cumulative updates yet they are initially deactivated by default. Administrators have the option to utilize Group Policy in order to enable these features and control the end-user experiences while activating default-off features.
Conclusion
By utilizing Group Policy to configure Windows Update for Business, IT administrators can effectively and efficiently handle updates on their managed windows devices. By creating deployment rings, controlling update offerings, and customizing user experiences, Maintaining device updates is possible for organizations, safe, and compliant with corporate policies. This method aids in upholding a superior level of productivity and protect sensitive data.

