- 24 January 2024
- 319
Understanding Heartburn: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Welcome to an extensive exploration of heartburn, a common yet often perplexing condition that impacts individuals worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the multifaceted aspects of heartburn, providing you with a nuanced understanding of its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive strategies.
What Is Heartburn?
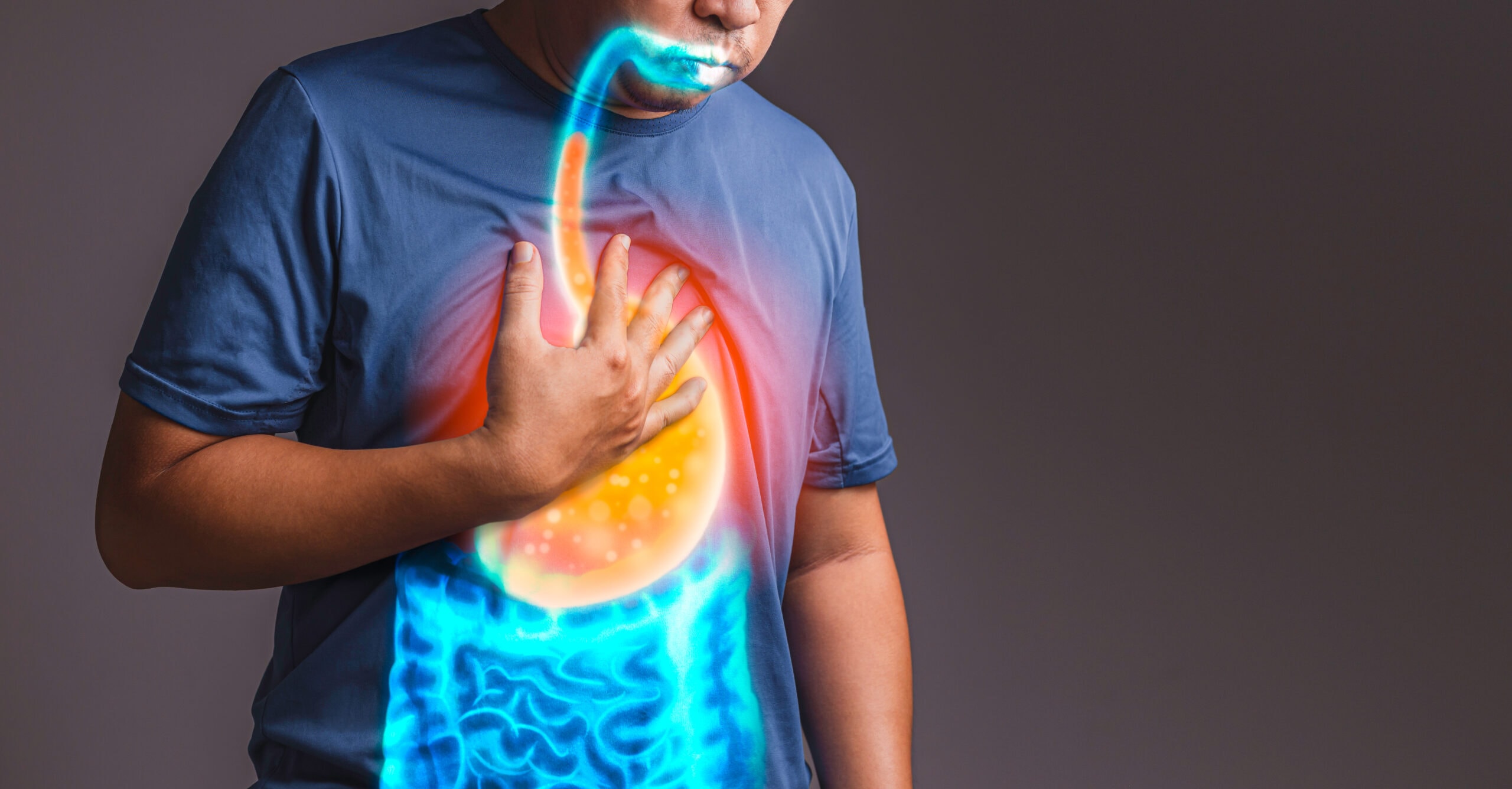
Decoding the Sensation: At its core, heartburn manifests as a burning discomfort in the chest, originating from the regurgitation of stomach acids into the esophagus. This irritation of the esophagus gives rise to a distinctive sensation, typically felt in the upper belly or chest.
Root Cause: The primary instigator of heartburn is acid reflux, a consequence of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) muscle failing to close properly. This failure permits stomach acids to flow back into the esophagus, triggering the characteristic discomfort.

Heartburn Symptoms
Unveiling the Signals: Recognizing heartburn involves a keen awareness of its distinct symptoms. These include the hallmark burning sensation in the middle of the chest and throat, pain after eating, and aggravation when bending or lying down.
Distinguishing Factors: Beyond the typical symptoms, it’s crucial to differentiate heartburn from a heart attack. While both may induce chest discomfort, heart attacks often entail sensations of tightening and pressure, whereas heartburn leans more towards a burning sensation.
Heartburn Causes
Peeling Back the Layers: A comprehensive understanding of the factors contributing to heartburn unveils insights into effective prevention.
LES Valve Dysfunction: A malfunctioning LES valve plays a pivotal role in permitting stomach acid to back up into the esophagus. The reasons behind LES weakness are diverse, ranging from frequent large meals to being overweight or harboring a hiatal hernia.
Risk Factors: Certain foods and lifestyle choices can relax the LES or increase stomach acid, elevating the risk of heartburn. Understanding these factors empowers individuals to make informed dietary and lifestyle decisions that can mitigate the likelihood of heartburn episodes.
Comparative Analysis: Explore the distinctions between heartburn, acid reflux, and indigestion through a comprehensive comparative table, shedding light on their unique characteristics.

Heartburn Diagnosis
Navigating Diagnostic Avenues: Persistent heartburn may necessitate a closer look through various diagnostic tests.
X-ray Insights: X-ray examinations, often involving the consumption of a barium solution, provide a visual representation of the upper gastrointestinal tract. This allows healthcare professionals to identify potential defects that may contribute to heartburn.
Endoscopic Exploration: Endoscopy, a procedure involving the insertion of a tiny camera down the throat, offers a direct view of the upper GI tract. This aids in the identification of issues contributing to heartburn and facilitates a more accurate diagnosis.
Ambulatory Acid Probe and Esophageal Motility Testing: Sophisticated tests such as ambulatory acid probe monitoring and esophageal motility testing provide valuable data on stomach acid reflux and esophageal movement. These tests are instrumental in diagnosing conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Heartburn Treatment
Navigating the Treatment Landscape: A nuanced understanding of how to manage heartburn is crucial for those seeking relief.
Over-the-Counter Solutions: Antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors are common over-the-counter options that offer relief. However, judicious use is essential to avoid potential side effects, such as constipation, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
Prescription Medications and Surgical Interventions: For cases where over-the-counter options fall short, healthcare professionals may consider prescription medications or even surgery. Surgical interventions become necessary in instances where other treatments prove ineffective or in cases of severe complications.

Heartburn Complications
Recognizing Warning Signs: Severe heartburn may lead to complications, necessitating prompt medical attention.
Indicators of Severity: Warning signs encompass confusion, chest tightness, bleeding, sore throat, fever, irregular heartbeat, weakness, or unusual fatigue. Chest pain, pressure, or burning that persists despite medications and lifestyle changes should prompt immediate medical assistance.
Heartburn Prevention
Proactive Measures for a Healthy Future: Preventing heartburn involves adopting lifestyle changes and cultivating healthy habits.
Weight Management and Dietary Choices: Maintaining a healthy weight and making mindful food choices can significantly reduce the risk of heartburn. Avoiding trigger foods and adopting habits like eating smaller meals throughout the day contribute to overall digestive health.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Practical tips, such as waiting three hours after eating before lying down or elevating the head of the bed, can make a substantial difference in preventing heartburn episodes.

Takeaways
Empowering Individuals: Understanding the fundamentals of heartburn empowers individuals to take charge of their digestive health.
Occasional vs. Chronic: While occasional heartburn is not life-threatening and can be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications, chronic cases, if left untreated, may lead to severe complications.

