- 24 January 2024
- 182
Understanding Diarrhea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
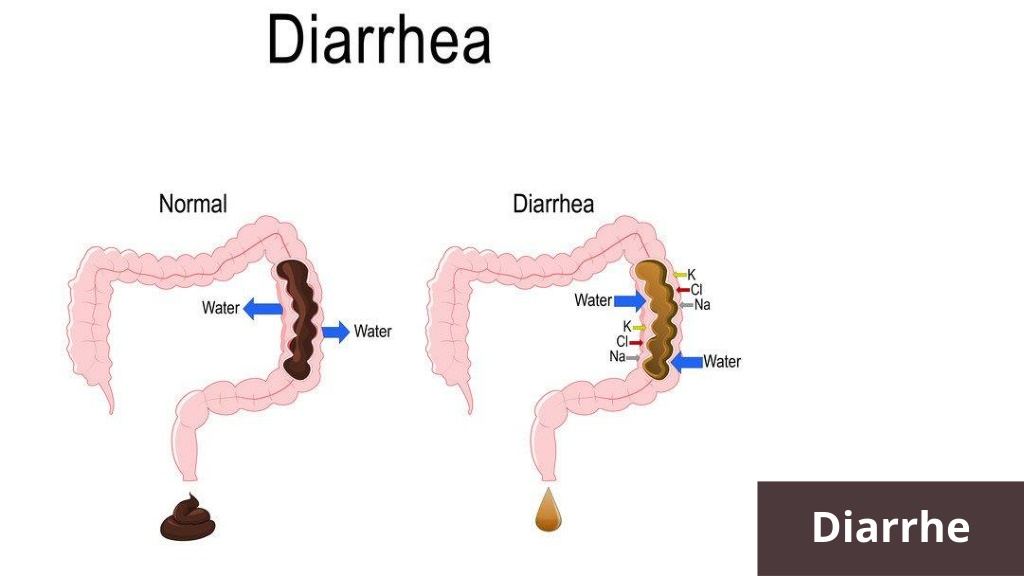
What Is Diarrhea?
Diarrhea occurs when bowel movements become loose and watery, often accompanied by an urgent need to use the restroom. It is a common condition that is usually not considered serious.

Diarrhea Causes
Diarrhea can be triggered by various factors, with viral infections being a common culprit, often referred to as “intestinal flu” or “stomach flu.” Other causes include allergies to certain foods, diseases of the intestines (such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis), consumption of irritating foods, bacterial infections (leading to food poisoning), laxative abuse, and even intense physical activities like running, which may result in “runner’s diarrhea.”

Diarrhea Symptoms
- Bloating in the Belly: Diarrhea may be accompanied by a feeling of fullness and bloating in the abdominal area.
- Thin or Loose Stools: The consistency of bowel movements changes, manifesting as thin or loose stools.
- Watery Stools: Diarrhea often involves the passage of watery stools, reflecting an abnormal increase in fluid content.
- Urgent Bowel Movements: An intense and urgent need to have a bowel movement characterizes episodes of diarrhea.
- Nausea: The sensation of queasiness or an inclination to vomit may accompany diarrhea.
- Vomiting: In some cases, individuals experiencing diarrhea may also vomit as a response to digestive distress.
Serious Symptoms of Diarrhea
- Blood or Mucus in Stools: Presence of blood or mucus in stools requires immediate attention and medical evaluation.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without apparent cause can be a red flag for underlying health issues.
- Dehydration Risks: If watery stools occur more than three times a day, and fluid intake is inadequate, dehydration may pose a serious threat.
When to See a Doctor for Diarrhea
Certain warning signs necessitate immediate medical attention. If you observe blood in your diarrhea, experience a high fever lasting more than 24 hours, or encounter diarrhea persisting beyond 2 days, seek medical advice. Other red flags include severe abdominal pain, especially in the right lower quadrant, or diarrhea after returning from a foreign country.
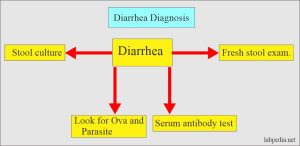
Diarrhea Diagnosis
To identify the cause of diarrhea, doctors may inquire about your medical history, recent dietary intake, and conduct a physical examination for signs of dehydration or abdominal pain. Diagnostic tests such as blood tests, colonoscopy, or stool tests may be employed for a more accurate diagnosis.
Treatment for Diarrhea
When it comes to addressing diarrhea, effective management involves a combination of treatments and relief measures. Explore the strategies to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery:
1. Mild Cases:
- Hydration: Drink at least six 8-ounce glasses of fluids daily to prevent dehydration.
- Electrolyte Replacement: Opt for electrolyte replacement drinks or non-caffeinated sodas to restore electrolyte balance.
- Dietary Adjustments: Choose easily digestible foods and avoid irritating substances.
2. Over-the-Counter Medications:
- Bismuth Subsalicylate or Loperamide: Adults can use these medications, available in liquid or tablet forms, for symptom relief.
3. Liquid Probiotics:
- Incorporate liquid probiotics into your routine to support gut health and aid in recovery.

Relief From Diarrhea Symptoms
Relief From Diarrhea Symptoms:
- Warm Baths or Sitz Baths: Soothe discomfort and alleviate soreness in the rectal area.
- Topical Applications: Consider using hemorrhoid cream or petroleum jelly for relief.
5. When to See a Doctor:
Seek medical attention if:
- Diarrhea persists for more than 3 days.
- Blood is present in diarrhea or stools appear black and tarry.
- High fever (above 101°F) lasts more than 24 hours.
- Nausea or vomiting hinders fluid replacement.
- Severe abdominal pain or discomfort is experienced.
- Diarrhea follows international travel.

6. Chronic Diarrhea:
If diarrhea persists beyond 4 weeks, a thorough examination is essential. Provide your doctor with detailed information about:
- Duration and patterns of diarrhea.
- Factors that worsen or improve symptoms.
- Stool characteristics (bloody, oily, fatty, or watery).
- Other accompanying symptoms and their duration.
- Family history of chronic diarrhea.
- Recent travel history and unusual food consumption.
- Medications or supplements being taken.
- Any significant weight loss.
Comprehensive management involves a tailored approach based on the severity and underlying causes. Timely medical attention ensures appropriate care and minimizes potential complications associated with prolonged or unresolved diarrhea.
| Aspect | Acute Diarrhea | Chronic Diarrhea |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Typically lasts 2-3 days | Persists for more than 4 weeks |
| Causes | Viral infections, allergies, digestive disorders | Varied, may require in-depth medical evaluation |
| Symptoms | Loose stools, nausea, urgent bowel movements | Prolonged discomfort, potential weight loss |
| Treatment Options | Over-the-counter medicines, hydration | Comprehensive diagnosis, specialized treatment |
| Relief Measures | Warm baths, creams | Addressing underlying causes for long-term relief |
| Medical Attention | If symptoms persist for more than 3 days | Immediate attention for prolonged symptoms |
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding diarrhea is paramount for effective management and timely intervention. While it is a common and often transient condition, being aware of its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for ensuring a swift recovery and preventing complications.
From viral infections and allergies to digestive disorders and intense physical activities, the causes of diarrhea are diverse. Recognizing the symptoms, including bloating, watery stools, and urgent bowel movements, empowers individuals to seek appropriate care when needed.
Treatment strategies range from hydration and dietary adjustments for mild cases to over-the-counter medications like bismuth subsalicylate or loperamide for symptom relief. Liquid probiotics and relief measures such as warm baths provide additional support. Knowing when to seek medical attention is vital. Persistent symptoms, the presence of blood or mucus in stools, and signs of dehydration warrant prompt consultation with a healthcare professional. In cases of chronic diarrhea lasting beyond 4 weeks, a comprehensive examination is necessary, with detailed information about symptoms, lifestyle, and medical history. By following these guidelines, individuals can navigate the challenges of diarrhea with knowledge and care, ensuring a balanced approach to recovery. Remember, effective management involves a combination of self-care measures and professional guidance, ultimately promoting overall well-being.

