- 22 February 2024
- 420
The Truth About Clogged Ears: Causes Revealed

Understanding the Anatomy of the Ear
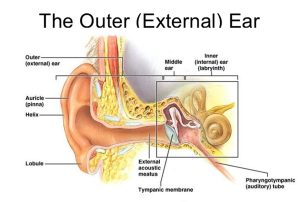
The human ear is an intricate organ responsible for both hearing and balance. It comprises three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Each component plays a crucial role in the auditory process. Understanding the anatomy of the ear is essential in comprehending the various factors that can lead to clogged ears. Explore More About (Teeth And Bones Health)
The Outer Ear
The outer ear consists of the pinna, the ear canal, and the eardrum (tympanic membrane). Its primary function is to collect sound waves and channel them into the ear canal towards the eardrum. Any blockages or obstructions in the ear canal can disrupt this process, leading to symptoms of clogged ears.
The Middle Ear
Behind the eardrum lies the middle ear, which contains three small bones known as the ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones transmit vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical signals that are interpreted by the brain. Conditions affecting the middle ear, such as infections or fluid buildup, can result in a sensation of fullness or congestion in the ears.
The Inner Ear
The inner ear is composed of the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular nerve. It plays a crucial role in both hearing and balance. The cochlea is responsible for converting sound vibrations into nerve impulses, while the semicircular canals aid in maintaining equilibrium. Disorders of the inner ear, such as Meniere’s disease, can cause symptoms of ear fullness and pressure.
Common Causes of Clogged Ears
Clogged ears can occur due to various underlying factors, ranging from mild to more severe conditions. Here are some of the most common causes:
Earwax Buildup
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is produced by glands in the ear canal to lubricate and protect the ear from dust, bacteria, and other foreign particles. However, excessive earwax accumulation can lead to blockages, causing symptoms such as hearing loss, earache, and a sensation of fullness in the ear.
Fluid Accumulation
Fluid buildup in the middle ear, often resulting from infections such as otitis media or sinusitis, can cause the Eustachian tube to become blocked. This can lead to a feeling of pressure or congestion in the ears, along with symptoms like decreased hearing and discomfort.
Allergic Reactions
Allergies can trigger inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, leading to congestion and clogged ears. Common allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can exacerbate symptoms, particularly during allergy season.
Respiratory Infections
Viral or bacterial infections, such as the common cold or flu, can affect the respiratory system and lead to symptoms of congestion and ear fullness. The Eustachian tube may become swollen or blocked, preventing proper drainage and ventilation of the middle ear.
Foreign Objects
Inserting foreign objects into the ear canal, such as cotton swabs or small toys, can push earwax deeper into the ear and cause blockages. Additionally, sharp objects or insects that inadvertently enter the ear can cause pain, irritation, and clogged ears.

Treatment Options for Clogged Ears
The appropriate treatment for clogged ears depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
Ear Irrigation
For earwax buildup, gentle irrigation with warm water or saline solution may help soften and remove the excess wax. However, it’s essential to exercise caution and avoid using sharp objects or cotton swabs, as they can push the wax further into the ear canal and potentially damage the eardrum.
Decongestants
Over-the-counter decongestant medications can help alleviate symptoms of congestion and sinus pressure, which may indirectly relieve clogged ears. However, these medications should be used cautiously and according to the manufacturer’s instructions, as prolonged use can lead to rebound congestion.
Antihistamines
Antihistamine medications can be beneficial for treating clogged ears caused by allergic reactions or hay fever. They work by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical released by the immune system in response to allergens, thereby reducing inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes.
Ear Drops
Commercially available ear drops containing hydrogen peroxide, glycerin, or olive oil can help soften and dislodge earwax, making it easier to remove. These drops should be used as directed and may require multiple applications over several days for optimal results.
Professional Cleaning
In cases of stubborn or impacted earwax, a healthcare professional may perform ear irrigation or manual removal using specialized instruments under magnification. This procedure is typically safe and effective when performed by a trained professional.
Surgical Intervention
In rare instances where clogged ears are caused by structural abnormalities or chronic conditions such as cholesteatoma, surgery may be necessary to correct the underlying problem. This may involve procedures such as tympanoplasty, mastoidectomy, or insertion of ventilation tubes.

Preventive Measures to Avoid Clogged Ears
While some causes of clogged ears may be unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and maintain ear health:
Practice Good Ear Hygiene
Avoid inserting cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other objects into your ears, as this can push earwax deeper into the ear canal and cause blockages. Instead, clean the outer ear with a soft cloth or tissue and allow the ear to naturally expel excess wax.
Protect Your Ears
Wear earplugs or earmuffs when exposed to loud noises or environments with excessive noise levels, such as concerts, construction sites, or sporting events. Prolonged exposure to loud sounds can damage the delicate structures of the inner ear and increase your risk of hearing loss.
Maintain Nasal Health
Keep your nasal passages clear and moisturized by using saline nasal sprays or performing nasal irrigation with a neti pot. This can help prevent congestion and inflammation in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, reducing your risk of clogged ears.
Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain proper hydration levels and promote healthy mucous membranes. Adequate hydration can help thin and loosen mucus secretions, making it easier for the Eustachian tubes to drain and equalize pressure in the ears.
Seek Prompt Medical Attention
If you experience persistent or severe symptoms of clogged ears, such as sudden hearing loss, severe pain, or discharge from the ear, seek medical attention from a qualified healthcare professional. Early intervention can help prevent complications and facilitate prompt resolution of the underlying problem.
Treatment Options for Clogged Ears
| Treatment Option | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ear Irrigation | Gentle flushing of the ear canal with warm water or saline solution to remove excess earwax. | Effective for mild to moderate earwax buildup. | Risk of eardrum perforation if not performed correctly. |
| Decongestants | Over-the-counter medications that help reduce congestion and sinus pressure, indirectly alleviating clogged ears. | Provides rapid relief from congestion. | May cause side effects such as increased heart rate or elevated blood pressure. |
| Antihistamines | Medications that block the action of histamine, reducing inflammation and congestion in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. | Effective for allergic reactions or hay fever. | Can cause drowsiness or dry mouth in some individuals. |
| Ear Drops | Commercially available drops containing hydrogen peroxide, glycerin, or olive oil to soften and dislodge earwax. | Convenient and easy to use at home. | May require multiple applications over several days for optimal results. |
| Professional Cleaning | Manual removal of impacted earwax by a healthcare professional using specialized instruments. | Safe and effective when performed by a trained professional. | Requires a visit to a healthcare facility. |
| Surgical Intervention | Surgical procedures to correct structural abnormalities or chronic conditions causing clogged ears. | Provides long-term resolution for severe cases. | Involves risks associated with anesthesia and surgery. |
Conclusion
Clogged ears can be a bothersome and uncomfortable condition, but understanding the underlying causes and appropriate treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and restore ear health. By practicing good ear hygiene, protecting your ears from excessive noise, and seeking timely medical attention when needed, you can minimize your risk of developing clogged ears and maintain optimal auditory function. Remember, your ears play a vital role in communication and balance, so it’s essential to take care of them.

