- 11 December 2023
- 2140
Regeneration: Exploring Renewal in Biology, Ecology, and Urban Development

Introduction
Regeneration, a fundamental process found in nature and human-made systems, embodies the concept of renewal, restoration, and growth. From biology’s cellular renewal to ecological rejuvenation and urban redevelopment, the principle of regeneration manifests in diverse ways across different domains.
Biology: The Miracle of Cellular Regeneration
In the realm of biology, regeneration denotes the remarkable ability of organisms to restore or replace damaged or lost cells, tissues, and even organs. Some species, like certain amphibians and invertebrates, showcase extraordinary regenerative capabilities, allowing them to regrow limbs or vital body parts. Scientists study these organisms to unlock the secrets behind cellular rejuvenation and its potential implications for human health and medicine.
Ecology: Reviving Ecosystems and Natural Harmony
Ecological regeneration involves the restoration of ecosystems following natural or human-induced disturbances. From reforestation after wildfires to the revival of marine habitats post-oil spills, nature demonstrates its capacity to heal and renew. Through conservation efforts, planting initiatives, and sustainable practices, humanity strives to support the regeneration of biodiversity and the delicate balance of ecosystems.
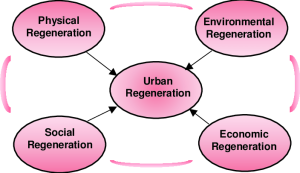
Urban Regeneration: Breathing New Life into Cities
In the urban landscape, regeneration signifies the revitalization of urban areas suffering from decay, neglect, or obsolescence. Through strategic urban planning, infrastructure improvements, and community engagement, cities undergo transformative regeneration projects. These initiatives aim to enhance livability, economic prospects, and social cohesion, turning once-neglected districts into vibrant, sustainable urban hubs.
Regeneration in Cultural Contexts
Beyond the scientific and environmental realms, the concept of regeneration holds cultural significance. Stories of personal growth, resilience, and renewal often revolve around the idea of regeneration, inspiring individuals to overcome challenges and transform their lives positively.
Challenges and Opportunities
While regeneration offers promise and hope, it also presents challenges. In biology, unlocking the full potential of human cellular regeneration for medical applications remains an ongoing endeavor. Ecological regeneration demands global cooperation to combat climate change and preserve natural resources. Urban regeneration faces obstacles such as funding constraints and community resistance, requiring innovative solutions and inclusive approaches.

Conclusion: Embracing Renewal and Growth
Regeneration, in its myriad forms, underscores the resilience and adaptability inherent in nature, societies, and individuals. Whether in the regeneration of tissues, ecosystems, or urban spaces, the principle of renewal offers hope for a better, more sustainable future. By fostering understanding, collaboration, and innovation, we can harness the power of regeneration to nurture growth and create lasting positive change.

