- 7 February 2024
- 149
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut and What to Do About It

Understanding the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, comprising trillions of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, is a fascinating ecosystem vital for human health. This intricate network of bacteria, viruses, and fungi plays a crucial role in various physiological functions, from digestion to immune regulation.

The Importance of Gut Health
Research underscores the importance of maintaining a balanced gut microbiome. A diverse array of gut bacteria is associated with reduced risks of chronic diseases such as diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and autoimmune conditions. Thus, nurturing a healthy gut ecosystem is fundamental for overall well-being.
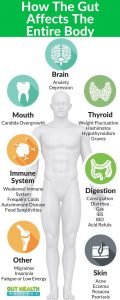
Effects on Health
The influence of the gut microbiome extends far beyond digestion. Emerging studies reveal connections between gut health and mental well-being, autoimmune disorders, cardiovascular health, and even cancer. A flourishing gut microbiome may contribute to improved physical and mental health, underscoring its pivotal role in holistic wellness.
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut
- Digestive Discomfort: Symptoms like bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, and heartburn often indicate an imbalance in gut bacteria. These disturbances signal the gut’s struggle to process food efficiently and eliminate waste.
- Dietary Factors: Consuming a diet high in processed and sugary foods can disrupt the balance of “good” and “bad” bacteria in the gut. Excessive sugar intake may trigger inflammation, paving the way for various health ailments.
- Unexplained Weight Changes: Unintentional weight loss or gain without alterations in diet or physical activity could be a red flag for gut health issues. Malabsorption, insulin resistance, or inflammation linked to gut imbalances may contribute to fluctuating weight.
- Sleep Disturbances: Poor sleep quality or insomnia may stem from disruptions in the gut microbiome. Research suggests a correlation between gut health, sleep patterns, and chronic fatigue, highlighting the bidirectional relationship between gut and brain health.
- Skin Conditions: Skin irritations like acne, eczema, or psoriasis may be linked to gut dysbiosis. Imbalances in gut bacteria can trigger immune responses that manifest as skin inflammation and aggravate existing dermatological conditions.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Dysfunctional gut microbiota can provoke systemic inflammation, compromising the immune system’s ability to distinguish between self and foreign antigens. This dysregulation may contribute to the onset or exacerbation of autoimmune diseases.
- Food Intolerances: Difficulty digesting certain foods, characterized by symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, or diarrhea, may indicate gut health issues. Imbalances in gut bacteria can disrupt digestive processes, leading to intolerance to specific food components.

Practical Strategies
Enhancing gut health naturally involves adopting lifestyle and dietary practices that support a balanced gut microbiome.
- Stress Management: Implement stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature to mitigate the detrimental effects of chronic stress on gut health.
- Quality Sleep: Prioritize sufficient and restorative sleep to promote optimal gut microbiome composition and function.
- Mindful Eating: Chew food slowly, savoring each bite, and opt for nutrient-dense, whole foods to nourish beneficial gut bacteria and minimize digestive discomfort.
- Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated with water and consume hydrating foods to support gut health and facilitate regular bowel movements.
- Probiotics and Prebiotics: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, along with prebiotic fibers found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Identify Food Intolerances: Keep a food diary and eliminate potential trigger foods to pinpoint and address food intolerances contributing to gut disturbances.
- Balanced Diet: Embrace a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and antioxidants to nourish the gut microbiome and optimize overall health. Explore More About (Story of Gallstones)

Superfoods for Gut Health
Certain foods possess gut-friendly properties, enhancing microbial diversity and supporting gut integrity.
- High-Fiber Foods: Incorporate legumes, whole grains, vegetables, nuts, and fruits into your diet to boost fiber intake and foster a thriving gut microbiome.
- Garlic: Harness the antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties of garlic to promote gut health and microbial diversity.
- Fermented Foods: Enjoy fermented delights like kimchi, sauerkraut, yogurt, and kefir to introduce beneficial probiotics into your gut ecosystem.
- Collagen-Boosting Foods: Indulge in collagen-rich foods such as bone broth, salmon skin, citrus fruits, and nuts to support gut lining integrity and overall health.
-
Image by: seebetterflorida.com
| Signs of an Unhealthy Gut | Ways to Improve Gut Health |
|---|---|
| Upset stomach | Lower stress levels |
| High-sugar diet | Adequate sleep |
| Unintentional weight changes | Chew food slowly |
| Sleep disturbances | Stay hydrated |
| Skin irritation | Take prebiotics/probiotics |
| Autoimmune conditions | Check for food intolerances |
| Food intolerances | Modify diet |
Conclusion
Prioritizing gut health is paramount for achieving holistic wellness. By adopting mindful lifestyle practices and nourishing dietary habits, individuals can cultivate a flourishing gut microbiome, paving the way for improved immunity, digestion, and overall vitality. With a deeper understanding of the gut microbiome’s intricacies, empowering individuals to embark on a journey towards optimal health becomes achievable and sustainable.


