- 8 January 2024
- 234
Hazards of Hypothermia ( Stay Warm in Cold Weather)
Understanding Hypothermia:
Hypothermia is a medical emergency that occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can produce heat, causing the body temperature to drop to a dangerously low level. Normal body temperature is around 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius), and hypothermia typically sets in when the body temperature drops below 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius). Prolonged exposure to cold weather, immersion in cold water, or wearing wet clothing in a cold environment are common causes of hypothermia. Symptoms include shivering, confusion, slurred speech, drowsiness, and eventually loss of consciousness. Prompt medical attention and rewarming methods, such as removing wet clothing, providing warm blankets, and offering warm fluids, are crucial in treating hypothermia.
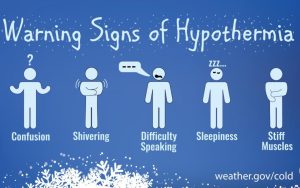
Warning Signs of Hypothermia:
Recognizing the warning signs of hypothermia is crucial for taking prompt action and preventing further complications. Common warning signs include:
Shivering:
Early stages of hypothermia often manifest with shivering as the body attempts to generate heat.
Cold or Pale Skin:
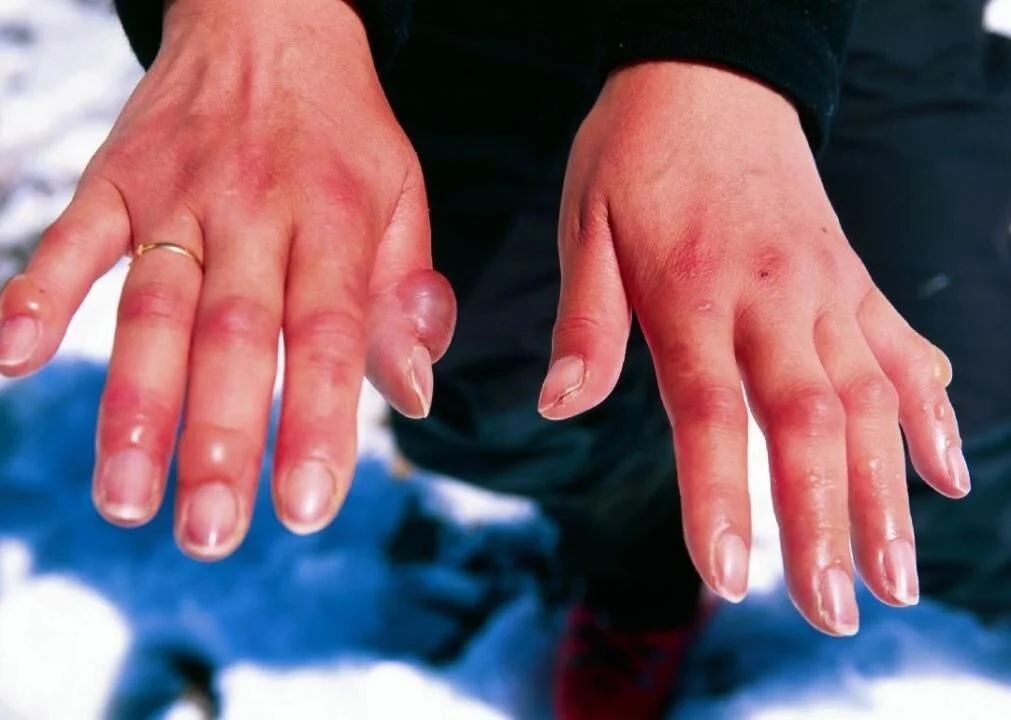
The skin may become cold, pale, or appear bluish, particularly in extremities like fingers and toes.
Slurred Speech:
Impaired motor functions and slurred speech can indicate the progression of hypothermia.
Weak Pulse:
As body temperature drops, the pulse may become weak or difficult to detect.
Slow or Shallow Breathing:
Respiratory rate may decrease, leading to slow or shallow breathing.
Confusion or Memory Loss:
Hypothermia can affect cognitive functions, leading to confusion, memory loss, and difficulty making decisions.
Fatigue or Drowsiness:
Individuals may experience extreme tiredness or drowsiness, hindering their ability to stay alert.
Stumbling or Lack of Coordination:
Reduced motor coordination, stumbling, or difficulty walking may occur.
Loss of Consciousness:
In severe cases, hypothermia can lead to loss of consciousness, requiring immediate medical attention.
Treatment to Protect Yourself:
The treatment of hypothermia involves gradual rewarming of the body while addressing potential complications. Here are essential steps in treating hypothermia:
- Move to a Warm Environment:
- Get the person out of the cold and into a warm, dry environment to prevent further heat loss.
- Remove Wet Clothing:
- Replace wet clothing with dry layers to minimize heat loss. Focus on insulating the head, neck, and torso.
- Wrap in Blankets or Warm Clothing:
- Use blankets, sleeping bags, or warm clothing to cover the person and provide insulation.
- Use Warm Compresses:
- Apply warm compresses to areas that are prone to heat loss, such as the neck, chest, and groin.
- Provide Warm Liquids:
- Offer warm, non-alcoholic beverages to help raise the internal body temperature.
- Avoid Direct Heat:
- Avoid using direct heat sources like hot water bottles or heating pads, as these can cause burns in the individual’s compromised state.
- Monitor Breathing:
- Continuously monitor the person’s breathing and pulse. Perform CPR if necessary.
- Seek Medical Attention:
- If the person’s condition is severe, if they lose consciousness, or if their body temperature drops below 95°F (35°C), seek immediate medical attention.

It’s crucial to rewarm the person gradually to avoid complications such as “rewarming shock.” Rapid rewarming can lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure. Professional medical evaluation is essential for severe cases of hypothermia. Always prioritize safety, and if in doubt, seek medical assistance promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hypothermia is a serious medical condition that requires swift and appropriate intervention. Recognizing the warning signs, such as shivering, confusion, and cold skin, is essential for initiating treatment. The primary goal is to gradually rewarm the affected individual by moving them to a warm environment, removing wet clothing, and providing insulation with blankets or warm clothing. Avoiding direct heat sources and closely monitoring vital signs are crucial aspects of the treatment process. In severe cases or if the person loses consciousness, seeking immediate medical attention is imperative. Prevention through proper clothing, staying dry, and avoiding prolonged exposure to cold conditions is key to mitigating the risk of hypothermia. Overall, prompt and effective action is vital for ensuring the well-being of individuals affected by hypothermia.

