- 5 February 2024
- 89
Getting to Know Hiatus Hernia: The Basics Simplified
Understanding Hiatus Hernia
Hiatus hernia, also known as hiatal hernia, is a condition where a portion of the stomach protrudes into the chest through an opening (hiatus) in the diaphragm, the muscle separating the chest and abdomen. This displacement can lead to various symptoms and complications, making it essential to comprehend the causes, types, and available treatments.
Its Impact on Heartburn
Though hiatus hernia itself often remains asymptomatic, it can trigger gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD). GORD occurs when stomach acid leaks into the oesophagus, the tube responsible for carrying food to the stomach. The malfunction of the valve at the bottom of the oesophagus, often caused by a hiatus hernia, is a primary contributor to GORD.
Symptoms:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest or throat.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest.
- Sour Taste: An unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Swallowing Problems: Difficulty swallowing, known as dysphagia.
If you experience frequent and severe manifestations of GORD, it is advisable to consult a general practitioner for further evaluation and guidance.
Causes of Hiatus Hernia
While the precise cause of hiatus hernia remains unclear, certain factors may contribute to its development. Aging can lead to the weakening of the diaphragm, increasing the likelihood of a hernia. Additionally, pressure on the abdomen, possibly due to obesity or pregnancy, may play a role in its occurrence. In rare instances, newborns may experience hiatus hernia due to improper development of the stomach or diaphragm.
Affected Demographics
Hiatus hernia can affect individuals of any age, but certain demographics are more prone to its occurrence. Those over the age of 50, individuals carrying excess weight, and pregnant women are more susceptible. It’s estimated that approximately one-third of individuals over the age of 50 may have a hiatus hernia.
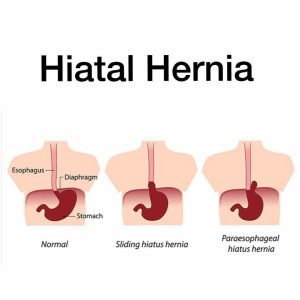
Types of Hiatus Hernia
There are two primary types of hiatus hernia:
- Sliding Hiatus Hernias:
- More common, accounting for over 80% of cases.
- Characterized by hernias that move up and down, in and out of the chest area.
- Para-Oesophageal Hiatus Hernias:
- Also known as rolling hiatus hernias.
- Involves part of the stomach pushing up through the hole in the diaphragm next to the oesophagus.
- Represents about 5 to 15% of hiatus hernia cases.
Diagnosing Hiatus Hernia
Diagnosing hiatus hernia involves various methods, including X-rays or endoscopy. X-rays can capture the movement of sliding hiatus hernias, while endoscopy utilizes a thin, flexible tube with a camera to examine the body’s internal structures. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a sliding hiatus hernia typically revolves around managing GORD symptoms, especially heartburn. Lifestyle changes and medications are commonly recommended, with surgery reserved for cases where symptoms persist or as an alternative to prolonged medication use. Want to Know Other Health Problems And Their Treatments
Lifestyle Recommendations:
- Dietary Changes: Opt for smaller, more frequent meals instead of three large meals a day.
- Posture After Eating: Avoid lying down, including going to bed, for at least three hours after eating or drinking.
- Identify Trigger Foods: Remove any foods or drinks from your diet that exacerbate symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you’re experiencing frequent and severe symptoms of GORD, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. Timely intervention can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent potential complications.

Complications and Long-Term Risks
While complications from hiatus hernia are rare, untreated cases can lead to long-term damage to the oesophagus. This may include the development of ulcers, scarring, and changes to the cells of the oesophagus, increasing the risk of oesophageal cancer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of hiatus hernia, its types, and the available interventions is vital for individuals experiencing symptoms. Regular medical check-ups are essential for those with persistent symptoms to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate management. By staying informed, individuals can actively participate in their healthcare and work towards a healthier, symptom-free life.

