- 15 July 2024
- 352
Edge Computing: Benefits and Challenges

Introduction:
As a technology enthusiast keen on exploring emerging trends, edge computing has emerged as a pivotal innovation reshaping how data is processed and managed. This article delves into the benefits of edge computing, its applications across various industries, and the challenges that organizations face in adopting and implementing this transformative technology.
1. Understanding Edge Computing
Define edge computing and its core principles. Explain how edge computing decentralizes data processing and storage, bringing computational capabilities closer to the data source or end-users, thereby reducing latency and enhancing real-time processing.
2. Benefits of Edge Computing
Explore the advantages of edge computing in modern applications. Discuss how edge computing:
- Enhances Speed and Efficiency: By processing data closer to the source, reducing the distance data needs to travel, and improving response times for applications requiring low latency, such as IoT devices and real-time analytics.
- Improves Reliability: Ensures continuous operation even in environments with limited or intermittent connectivity, enhancing reliability and performance for critical applications.
- Reduces Bandwidth Usage: Minimizes the strain on centralized networks by processing data locally, thereby reducing bandwidth costs and optimizing network efficiency.
- Facilitates Data Privacy and Security: Enhances data privacy and security by processing sensitive information locally, reducing exposure to potential cyber threats associated with transmitting data over networks.
3. Applications Across Industries
Examine the diverse applications of edge computing in various industries. Highlight use cases in:
- IoT and Smart Devices: Enabling real-time data processing for smart homes, wearable devices, and industrial IoT applications.
- Telecommunications: Optimizing network performance, enabling low-latency applications like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) streaming.
- Healthcare: Facilitating remote patient monitoring, medical diagnostics, and real-time healthcare data analytics at the point of care.
- Retail: Enhancing customer experiences through personalized marketing, inventory management, and real-time analytics in brick-and-mortar stores.
4. Challenges in Adopting Edge Computing
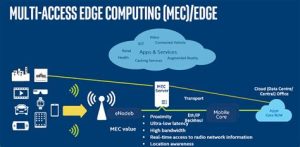
Discuss the challenges organizations face when adopting edge computing technology:
- Security Concerns: Securing distributed edge devices and data against cyber threats, ensuring data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Scalability Issues: Managing and scaling edge infrastructure to accommodate growing data volumes and diverse applications without compromising performance.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating edge computing solutions with existing IT systems and cloud infrastructure, ensuring seamless data flow and interoperability.
- Cost Considerations: Balancing the upfront costs of deploying edge infrastructure with long-term operational savings and ROI, optimizing resource allocation and budget planning.
5. Future Trends and Innovations
Conclude with a look at future trends and innovations in edge computing. Discuss advancements in:
- AI and Machine Learning at the Edge: Integrating AI capabilities into edge devices to enhance real-time decision-making and predictive analytics.
- 5G and Edge Computing Synergies: Leveraging 5G networks to support high-bandwidth, low-latency applications at the edge, enabling new use cases in autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
- Edge-to-Cloud Orchestration: Developing hybrid edge-to-cloud architectures for seamless data processing and workload management across distributed environments.
Informative Table: Key Benefits of Edge Computing
| Benefit | Description | Examples |
| Speed and Efficiency | Faster data processing and reduced latency | Real-time analytics, IoT applications |
| Reliability | Continuous operation in low-connectivity environments | Industrial automation, remote monitoring |
| Data Privacy and Security | Enhanced privacy and reduced cyber threats | Healthcare data, sensitive information processing |
| Bandwidth Optimization | Reduced strain on centralized networks | Video streaming, content delivery networks |
Comparative Table: Centralized Cloud vs. Edge Computing
| Aspect | Centralized Cloud | Edge Computing |
| Data Processing | Centralized, remote processing | Distributed, local processing |
| Latency | Higher latency due to distance from data source | Lower latency for real-time applications |
| Security | Potential data exposure during transmission | Enhanced security with local data processing |
| Scalability | Scaling challenges with increasing data volumes | Scalable edge infrastructure for local processing |
Conclusion: Embracing Edge Computing’s Potential
Edge computing offers substantial benefits in speed, efficiency, and reliability by decentralizing data processing and bringing computational capabilities closer to users and devices. Despite challenges such as security concerns and integration complexity, the transformative potential of edge computing across industries like IoT, healthcare, and retail is undeniable.
As organizations navigate these challenges and leverage innovations in AI, 5G, and hybrid architectures, embracing edge computing will pave the way for enhanced data-driven insights, real-time decision-making, and optimized operational efficiency in the digital age.

