- 29 February 2024
- 127
Learning about POTS: Ways to Diagnose and Treat Dizziness

Understanding POTS
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is a complex and often misunderstood condition characterized by a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Individuals with POTS typically experience a significant increase in heart rate upon standing, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, and fainting. While the exact cause of POTS remains elusive, several factors such as genetics, viral infections, and autoimmune disorders are believed to contribute to its development. Explore More About (Link between Covid And diabetes)
Diagnosing POTS
Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosing POTS can be challenging due to its heterogeneous nature and overlapping symptoms with other conditions. However, healthcare professionals often begin with a thorough clinical evaluation, which includes a detailed medical history and physical examination. Patients are typically asked about their symptoms, medical history, and any potential triggers that exacerbate their symptoms.
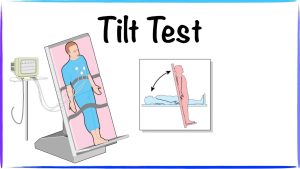
Tilt Table Test
One of the primary diagnostic tools for POTS is the tilt table test. During this procedure, the patient lies flat on a table, which is then tilted to an upright position. Continuous monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure helps identify abnormal changes in response to postural changes. A significant increase in heart rate (usually by 30 beats per minute or more) within the first 10 minutes of standing is indicative of POTS.
Autonomic Function Tests
Autonomic function tests, such as the Valsalva maneuver and sweat tests, may also be performed to assess the integrity of the autonomic nervous system. These tests help evaluate how the body responds to various stimuli and can provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of POTS.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be conducted to rule out other potential causes of symptoms, such as thyroid disorders, vitamin deficiencies, or autoimmune diseases. Additionally, specialized blood tests, including catecholamine levels and autoimmune markers, may help identify underlying abnormalities associated with POTS.
Treatment Approaches
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications is often the first line of treatment for individuals with POTS. This may include increasing fluid and salt intake to expand blood volume, wearing compression stockings to improve blood flow, and incorporating regular exercise to improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce symptoms.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Beta-blockers and vasoconstrictors are ceommonly used to control heart rate and blood pressure fluctuations, while fludrocortisone may be prescribed to enhance fluid retention and blood volume.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in managing POTS symptoms, particularly in improving muscle strength, endurance, and overall functional capacity. Exercises targeting the lower body, such as leg strengthening and aerobic conditioning, may help improve blood circulation and reduce symptoms of orthostatic intolerance.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT can be beneficial for individuals with POTS, especially those struggling with anxiety, depression, or coping with chronic symptoms. By addressing maladaptive thought patterns and implementing coping strategies, CBT aims to improve psychological well-being and enhance resilience in the face of chronic illness.
Treatment Options for POTS
| Treatment Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle Modifications | Includes dietary changes, increased fluid intake, salt supplementation, and physical activity. |
| Medications | Beta-blockers, vasoconstrictors, and fludrocortisone may be prescribed to manage heart rate and blood pressure. |
| Physical Therapy | Focuses on improving muscle strength, endurance, and cardiovascular fitness through targeted exercises. |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Addresses psychological factors such as anxiety and depression, aiming to improve coping mechanisms and overall well-being. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, POTS is a complex disorder that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and implementing appropriate interventions, individuals with POTS can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. From clinical evaluation to lifestyle modifications and pharmacological interventions, a multi-disciplinary approach is essential in addressing the diverse needs of patients with POTS. With ongoing research and advancements in medical care, there is hope for better outcomes and increased awareness of this debilitating condition.

